Antibiotics for Psoriasis: Treating Psoriasis with Topical and Oral Antibiotics
While Psoriasis, unlike other skin problems, is not infectious, antibiotics for psoriasis are often the proscribed treatment of this condition. They have been of great help to dermatologists for killing T cells, a form of white blood cells that became over stimulated which are harmful to the skin. This slows down the growth of Psoriasis infection.
High doses of antibiotics are a standard procedure for psoriasis outbreak, especially if caused by strep throat, and they are given in two forms – Topical and oral.
Natural Antibiotics in Foods
Topical Antibiotics for Psoriasis
Corticosteroid
This medication consists of antibiotic as well as disinfectant which maintains swelling of skin in its full control, making it among one of the most searched for antibiotic therapy for psoriasis. Less turn overs are located in the cells and also body immune system is maintained under control. Physicians suggest using this certain lotion two times in a day as well as not even more compared to that.
Topical Corticosteroid is additionally categorized as a type of steroids as well as lengthy- term usage of this lotion thins down the level of the skin and also could trigger various other troubles for the skin. Stay clear of suddenly terminating using this drug as it could subsequently trigger your psoriasis to flare. Prescription antibiotics for Psoriasis.
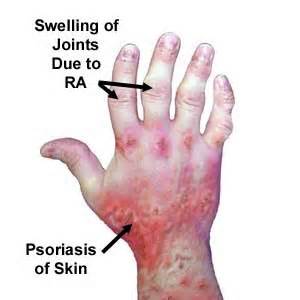

Imidazole
Imidazole contains flavohemoglobins, which protects bacteria from growth inhibition by metabolizing the nitic oxide. Apply imidazole antibiotics for psoriasis cream twice daily on the psoriasis-affected area for a period of two to nine months for a more beneficial effect. The Imidazole antibiotic treatment is one that is highly successful for psoriasis with clearing lasting for a longer period post treatment.
Oral Antibiotics
Rifampin
This form of antibiotic is to prevent and treat only bacterial infection on skin, like psoriasis, and works best on an empty stomach taken with a full glass of water. Rifampin is to be taken at evenly spaced interval for most effective result and must be continued until the prescription is finished.
Bacteria will continue to grow if the prescription is not followed properly. Remember to consult a physician or doctor for the right prescription to avoid from irregular or incorrect dosages, which in turn, leads to side effects like heartburn, nausea, or menstrual changes.
Zithromax
Zithromax is a form of macrolide antibiotics for psoriasis that help in preventing the growth of bacteria by interfering with the bacteria’s capability to create proteins. In cases of psoriasis, the turnover rate of the bacteria and skin growth is heightened, and this can be prevented with zithromax.
Recommended to be taken with food to reduce stomach upset and must not be taken together with aluminum and magnesium based antacids, as these antacids will prevent the antibiotic from being absorbed effectively from the intestine. Erythromycin also falls under the same class as Zithromax.
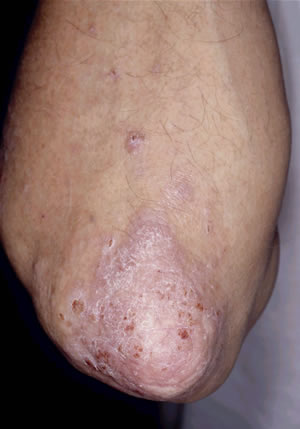 Psoriasis on the ellbow
Psoriasis on the ellbowLevaquin
Levaquin is a form of antibiotic that helps stop the growth of bacteria and fungi by preventing the multiplication and repair of the bacteria’s DNA genetic material. Standard dose is only once a day and to be taken at least 2 hours before or after any dosage of antacid.
Consult a physician or doctor if you are likely to combine other prescription with Levaquin as there are prominent side effects to it. For example, a combination of NSAIDS such as Aspirin with Levaquin will change your blood sugar level and increase your CNS stimulation, resulting in over-excitation.
Avelox
Avelox is a part of the quinolone antibiotics group and treats only bacterial infection, such as skin infection seen in psoriasis cases. Proper care need to be taken for the use of this group of antibiotics as it will, in some rare cases, cause tendon damage, even more so, if you are 60 years old and above. Overall,
Antibiotics for psoriasis are seldom the main treatment for psoriasis, as the effectiveness of it is vague in some cases of psoriasis, while in other patients it helps very mildly or don’t at all.
The Intricacies of Antibiotic Treatment for Psoriasis: Analysing the Risks, Costs and Efficacy
Understanding the Potential Risks and Side Effects of Long-Term Antibiotic Use in Psoriasis Treatment
Antibiotics have been widely used in medicine due to their effective fight against bacterial infections. However, their long-term use, especially in treating medical conditions like psoriasis, could potentially lead to some risks and side effects. Psoriasis sufferers may experience gastrointestinal problems, skin reactions, or even severe allergic reactions. Furthermore, it's essential to consider the risk of generating antibiotic-resistant bacteria which could further complicate the treatment in the long run.
Discussion on the Financial Cost of Antibiotics Treatment and Insurance Coverage
Psoriasis treatment, especially with antibiotics, can result in substantial costs. The exact amount will differ based on factors such as the required dosage and the length of treatment. Most health insurance companies do cover medically necessary treatments, which could potentially include antibiotics for psoriasis. However, as each insurance policy is different, patients should ensure they understand their coverage scope before proceeding with this treatment.
Interactions of Antibiotics with Other Psoriasis Medications or Treatments
Using antibiotics alongside other psoriasis treatments could result in interactions that may either reduce the effectiveness or increase certain side effects. Therefore, patients must thoroughly inform their healthcare providers about any other medications or supplements they are currently taking. It is also advisable to monitor any changes in health while under multiple treatments.
Comparative Success Rate of Antibiotics for Psoriasis Treatment
While antibiotics can undoubtedly help in treating psoriasis, their success against this skin condition has been comparatively less than other treatment options such as light therapy or topical treatments. Antibiotics aim to ward off any infections that could trigger psoriasis, rather than directly treating psoriasis. Therefore, their efficacy in psoriasis cases that are not infection-driven is significantly reduced.
Expectation Gauge: Timeline for Results from Antibiotic Treatment
Typically, patients may start to see results from antibiotic treatment for psoriasis within a few weeks. However, individual responses can vary, depending on factors like the severity of the psoriasis, the specific antibiotic used, and the patient's overall health. Therefore, it's crucial for patients to maintain regular consultations with their doctors throughout the treatment process.
Antibiotic Treatment Suitability for Different Types of Psoriasis
While some types of psoriasis, like guttate psoriasis, might respond positively to antibiotic treatment due to their connection to strep infections, others may not. It's crucial to determine the cause and type of psoriasis for an effective treatment plan. This is another reason why communication and consultation with healthcare providers is crucial for patients.
Natural Supplements: Lifestyle Changes Complementing Antibiotic Treatment
In addition to antibiotics, certain lifestyle changes can also significantly help manage psoriasis. A balanced diet rich in fruits, vegetables, lean proteins, and whole grains can support overall health and boost immunity. Moderate and regular exercise can help reduce stress and maintain a healthy weight, potentially reducing psoriasis flare-ups.
Suitability of Antibiotics for Psoriasis in Children, Pregnant Women, and Elderly Patients
Certain patient groups like children, pregnant women, and elderly patients may require special consideration for antibiotic treatment due to possible increased risks or side effects. It is always imperative to discuss treatment plans extensively with health care providers who would cater to the treatment course based on individual medical histories.
Management of Potential Psoriasis Flare-Ups during Antibiotic Treatment
For those experiencing flare-ups or worsening symptoms during antibiotic treatment, the first step should always be to alert their health care provider. Meanwhile, implementing coping mechanisms like moisture-locking skincare routines, minimal consumption of alcohol, and avoidance of known triggers can provide some relief. Regular check-ins with healthcare professionals can greatly assist in managing psoriasis and adjusting the course of treatment as required.
Antibiotic Resistance in the Treatment of Psoriasis
Over time, bacteria can develop resistance to antibiotics, making them less effective in treating psoriasis or any other bacterial infection. To mitigate this risk, patients should strictly adhere to their doctor's prescription, avoid unnecessary antibiotics use, and report any changes to their healthcare provider promptly.
Management of Potential Psoriasis Flare-Ups during Antibiotic Treatment
For those experiencing flare-ups or worsening symptoms during antibiotic treatment, the first step should always be to alert their health care provider. Meanwhile, implementing coping mechanisms like moisture-locking skincare routines, minimal consumption of alcohol, and avoidance of known triggers can provide some relief. Regular check-ins with healthcare professionals can greatly assist in managing psoriasis and adjusting the course of treatment as required.
In conclusion, while antibiotics can play a role in treating certain types of psoriasis, it’s essential to consider potential risks, costs, and efficacy and discuss with healthcare professionals to create an informed, comprehensive treatment plan. Moreover, embracing a healthy lifestyle and employing suitable management strategies for flare-ups can complement and enhance treatments.
National Institute of Arthritis and Musculoskeletal and Skin Diseases
Sitemap in alphabetical order
More informations about treatments of psoriasis
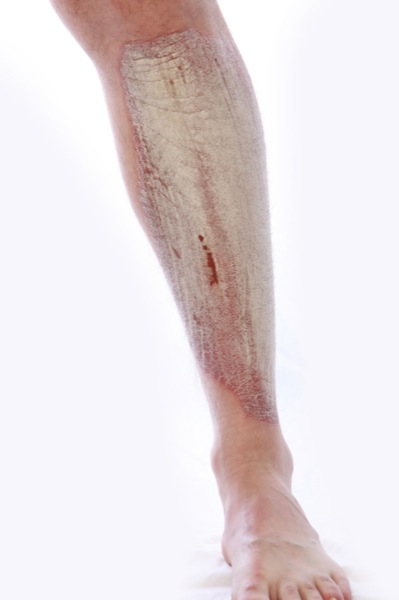 Psoriasis en la pierna
Psoriasis en la piernaPágina de inicio
Mapa del sitio
Mapa del sitio en orden alfabético
